What is Birth Control?
Birth control, also known as contraception, anti-conception, and fertility control, is a method or device used to prevent pregnancy. Although birth control has been used since ancient times, effective and safe contraception methods only became available in the 20th century.
Birth Control in Singapore
One of the most commonly practised birth control methods in Singapore is the rhythm method (sex only while you’re not ovulating) and withdrawal (pull out) method, which is not super effective. After all, sperm can be extremely tricky – they can live inside the vagina and the rest of the reproductive tract for up to around six days.
Another common method is male condoms. Condoms can be readily bought at any convenience store or supermarket and offer protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, they are only about 85 percent effective in preventing pregnancies (one of the lowest). The effectiveness of condoms depends on when and how it is put on and there is also a risk of condoms tearing during sex.
There are other birth control methods that have higher success rates – but they can cost more money, take more discipline to use or require more commitment. All require a doctor’s prescription after a thorough consultation.
Types of Birth Control Methods
These contraception options can be split into 2 major categories – Temporary and Permanent.
| Contraception | Temporary (Reversible) | Permanent |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Hormonal birth control (Short-acting) – Birth control pill – Birth control patch – Contraception injection Intrauterine device (Long-acting) | Tubal ligation |
To help you along, we discuss the common contraceptive methods in Singapore, their mode of action, effectiveness, pros and cons. Here’s what every responsible man and woman should know.
1. Birth control pill

What is birth control pill?
Birth control pills are medications you take by mouth to prevent pregnancy. Hormones in the pills prevent pregnancy by:
- stopping or reducing ovulation (the release of an egg from an ovary)
- thickening cervical mucus to keep sperm from entering the uterus
- thinning the lining of the uterus so that a fertilized egg is less likely to attach
Effectiveness:
Used perfectly, most birth control pills are 99 percent effective at preventing pregnancy. In “real life” conditions (e.g. occasional missed or late dose), the birth control pills are about 91 percent effective.
Pros:
- you don’t need to use the pill every time you have sex in order to stay protected, unlike condoms
- fertility returns immediately when you stop taking it
- lower risk of ovarian and endometrial cancer
- non-contraceptive benefits such as:
- helping to regulate the menstrual cycle;
- manage acne; and
- improve PMS symptoms.
Cons:
- not for those who hate popping pills
- have to take the pill every day for it to work properly
- not suitable for women with certain existing health problems, or medications
2. Birth control patch

What is birth control patch?
The birth control patch is a thin skin patch that is worn anywhere on the abdomen, thigh, buttocks or arm and changed weekly. The patch releases a daily dose of hormones (estrogen and progestin) through the skin into the bloodstream to prevent the ovaries from releasing eggs each month (ovulation). It also thickens the cervical mucus, which keeps sperm from getting to the egg. (Source: MayoClinic)
Effectiveness:
Used perfectly, most birth control patches are 99 percent effective at preventing pregnancy. In “real life” conditions (e.g. forget to replace the patch or patch is not stuck properly), the birth control patches are about 91 percent effective.
Pros:
- good alternative for people who find pill-popping a hassle
Cons:
- the patch is not transparent
- might be uncomfortable due to Singapore’s hot and humid weather
- some women get insecure because they are unsure if it will fall off
3. Contraceptive injection
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1081205870-52fb358b5ca148abb8d35d48b1f7ffb7.jpg)
What is contraceptive injection?
The contraceptive injection is a shot of hormones given by your GP or gynae to prevent ovulation and has to be repeated every 90 days.
Effectiveness:
Used perfectly, most contraceptive shots are more than 99 percent effective at preventing pregnancy. In “real life” conditions (e.g. missed or late shots), the contraceptive shots are about 94 percent effective.
Pros:
- good alternative for people who find pill-popping or changing patches a hassle
- suitable for breastfeeding mums
- light or possibly no periods after a year
Cons:
- weight gain and irregular bleeding in the first three months are possible as your body adjusts
- takes 6 to 12 months to regain fertility after you stop the injections
4. Intrauterine device (IUD)

What is IUD?
An IUD, or the coil, is a small T-shaped device that is inserted and left in your uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some IUD types work by releasing small amounts of hormones, while others use copper to trigger your immune system to prevent pregnancy.
Effectiveness:
More than 99 percent effective at preventing pregnancy
Pros:
- can be left in the womb for up to five years
- fertility returns immediately once you remove it
Cons:
- may cause irregular bleeding or spotting
- usually not recommended as the first choice for anaemic women or those who have heavy periods
- there is a small risk that the IUD may fall out and cause an infection during the insertion (in rare instances)
- difficulty in removing the device.
5. Tubal ligation
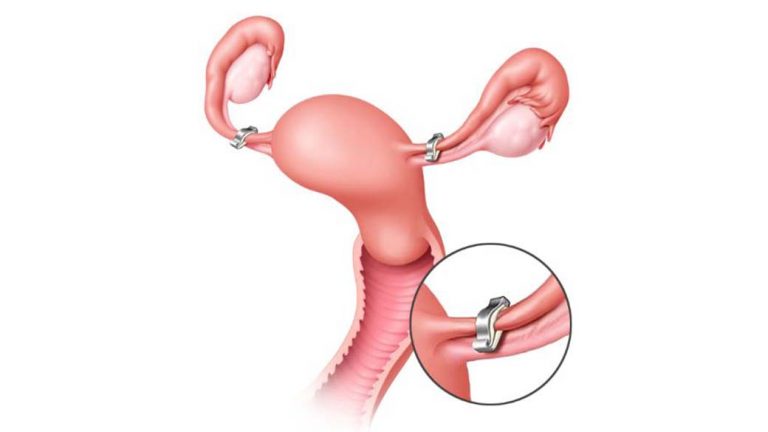
What is Tubal Ligation?
During a tubal ligation (female sterilization), the fallopian tubes are cut, tied or blocked to permanently prevent pregnancy. Tubal ligation prevents an egg from travelling from the ovaries through the fallopian tubes and blocks sperm from travelling up the fallopian tubes to the egg. (Source: Mayo Clinic)
Effectiveness:
More than 99 percent effective at preventing pregnancy
Pros:
- a good option for women who are certain that they no longer want more children
- does not affect your hormone levels and you’ll still have periods
Cons:
- irreversible
- small risk of complications as with any surgery, such as internal bleeding, infection or damage to other organs
Which Birth Control Method Is Right for Me
When it comes to birth control, you have options and there are no bad options.
What suits you will depend on factors such as your age, frequency of sexual activity, family history regarding certain illnesses, comfort level when using a particular method, and level of desire to be pregnant in the future.
And remember, you don’t have to figure it out all on your own. Before settling on any option, do your own research or speak with your doctor to figure out which contraceptive will work best for you.
At Siena, you can speak to one of our female doctors in the privacy and comfort of your home, order your contraceptives online and get them delivered to your door in discreet packaging. Feel free to reach out!